 Largemouth Bass are usually green with dark blotches that form a horizontal stripe along the middle of the fish on either side. They have a nearly divided dorsal fin with the anterior portion containing nine spines and the posterior portion containing 12 to 13 soft rays. Their upper jaw reaches far beyond the rear margin of the eye. The Lake Fork spawn begins in the spring when water temperatures reach about 60 degrees. This could occur as early as February or as late as May. Largemouth bass prefer to nest in quieter, more vegetated water but will use any substrate besides soft mud, including submerged logs.
Largemouth Bass are usually green with dark blotches that form a horizontal stripe along the middle of the fish on either side. They have a nearly divided dorsal fin with the anterior portion containing nine spines and the posterior portion containing 12 to 13 soft rays. Their upper jaw reaches far beyond the rear margin of the eye. The Lake Fork spawn begins in the spring when water temperatures reach about 60 degrees. This could occur as early as February or as late as May. Largemouth bass prefer to nest in quieter, more vegetated water but will use any substrate besides soft mud, including submerged logs.
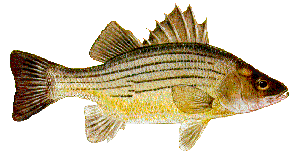 Yellow Bass are sometimes confused with white bass but there are several distinguishing characteristics. First, the belly may take on a yellow color, from which the species derives its common name. Second, the two lowermost strips are distinctively broken just posterior to the middle. Also, the second and third anal spines are approximately equal in length.
Yellow Bass are sometimes confused with white bass but there are several distinguishing characteristics. First, the belly may take on a yellow color, from which the species derives its common name. Second, the two lowermost strips are distinctively broken just posterior to the middle. Also, the second and third anal spines are approximately equal in length.
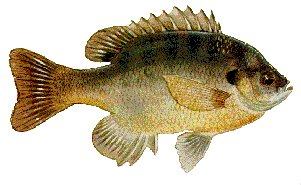 Bluegills may be distinguished from other sunfish by the dark spot at the base of the dorsal fin, vertical bars on their sides, and a relatively small mouth. The spiny dorsal fin usually has 10 (but may have as many as 11 or as few as 9) and is broadly connected to the soft dorsal. The anal fin has three spines.
Bluegills may be distinguished from other sunfish by the dark spot at the base of the dorsal fin, vertical bars on their sides, and a relatively small mouth. The spiny dorsal fin usually has 10 (but may have as many as 11 or as few as 9) and is broadly connected to the soft dorsal. The anal fin has three spines.
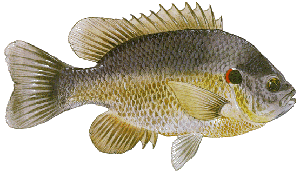 The Redear is a deep-bodied sunfish with a relatively small mouth. Color ranges from dark olive green above to almost white on the belly. The sides are usually yellow to green. The spinous dorsal fin, which is anterior to the soft dorsal fin, is normally equipped with 10 spines, although 9 or 10 spines are sometimes observed, and it is broadly connected to the soft dorsal fin.
The Redear is a deep-bodied sunfish with a relatively small mouth. Color ranges from dark olive green above to almost white on the belly. The sides are usually yellow to green. The spinous dorsal fin, which is anterior to the soft dorsal fin, is normally equipped with 10 spines, although 9 or 10 spines are sometimes observed, and it is broadly connected to the soft dorsal fin.
 White Crappie is deep-bodied and silvery in color, ranging from silvery-white on the belly to a silver-green or even dark green on the back. There are several vertical bars on the sides. The dorsal fin has a maximum of 6 spines. White crappie nest in the spring, generally when water temperatures reach 65 to 70 degrees.
White Crappie is deep-bodied and silvery in color, ranging from silvery-white on the belly to a silver-green or even dark green on the back. There are several vertical bars on the sides. The dorsal fin has a maximum of 6 spines. White crappie nest in the spring, generally when water temperatures reach 65 to 70 degrees.
 Black Crappie easily confused with the white crappie. However, it is deeper bodied than the white crappie, and silvery-green in color. There are no distinct vertical bars, rather there are irregular black blotches. The dorsal fin has 7 or 8 spines.
Black Crappie easily confused with the white crappie. However, it is deeper bodied than the white crappie, and silvery-green in color. There are no distinct vertical bars, rather there are irregular black blotches. The dorsal fin has 7 or 8 spines.
 Channel Catfish are easily distinguished from all others, except blue catfish, by their deeply forked tail fin. Unlike flathead catfish, the upper jaw projects beyond the lower jaw. Coloration is olive-brown to slate-blue on the back and sides, shading to silvery-white on the belly.
Channel Catfish are easily distinguished from all others, except blue catfish, by their deeply forked tail fin. Unlike flathead catfish, the upper jaw projects beyond the lower jaw. Coloration is olive-brown to slate-blue on the back and sides, shading to silvery-white on the belly.
 Flathead Catfish have a smooth, scale less skin, whisker-like barbells around the mouth, and long, sharp spines on the dorsal (back) fin and one on each side of the pectoral (shoulder) find. The belly is usually pale yellow or cream colored. The head is broadly flattened, with a projecting lower jaw. The tail fin is only slightly notched.
Flathead Catfish have a smooth, scale less skin, whisker-like barbells around the mouth, and long, sharp spines on the dorsal (back) fin and one on each side of the pectoral (shoulder) find. The belly is usually pale yellow or cream colored. The head is broadly flattened, with a projecting lower jaw. The tail fin is only slightly notched.
 Common Carp are generally considered a nuisance by North American anglers, but they are prized as sport fish in Europe, as they are excellent fighters. Although flavor varies with the quality of the water from which fish were captured, their sheer abundance has made them an important food fish in some areas. The Texas rod-and-reel record is currently 43.13 pounds. The North American record exceeds 57 pounds.
Common Carp are generally considered a nuisance by North American anglers, but they are prized as sport fish in Europe, as they are excellent fighters. Although flavor varies with the quality of the water from which fish were captured, their sheer abundance has made them an important food fish in some areas. The Texas rod-and-reel record is currently 43.13 pounds. The North American record exceeds 57 pounds.
 Smallmouth Buffalo have a back and sides of light brown, or are dark with a coppery or greenish tint. The belly is pale yellow to white. Scales are large, and the species is sometimes confused with common carp. They lack the barbells of Carp, Smallmouth buffalo, as opposed to bigmouth buffalo; have a distinctive sucker-type mouth, oriented downward.
Smallmouth Buffalo have a back and sides of light brown, or are dark with a coppery or greenish tint. The belly is pale yellow to white. Scales are large, and the species is sometimes confused with common carp. They lack the barbells of Carp, Smallmouth buffalo, as opposed to bigmouth buffalo; have a distinctive sucker-type mouth, oriented downward.
 Blue Catfish
Blue Catfish

